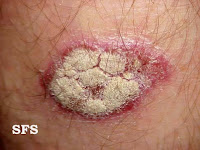
defintion...
it's chronic relapsing & remitting skin diseases
where red raised plaques covered by white scales.
Precpitating factors:
1-truma 2-infection 3-AIDS
4-hormonal factors[pregnancy,contraceptive pills]
5-cold weather 6-smoking & alchol
7-emotional psoriasis
Pathological features ....
1)acanthosis= hyperkeratosis =marked thickning of the epidermis
2)abscence of the granular cell layer.
3)parakeratosis = retention of nuclei in the horny layer.
4)monro microabscess= accumulation of leucocytes.
5)dilated capillary loops.
General features....
*exposure to sunlight and UV radiation improve psoriasis.
*drugs aggrevate the condition of psoriasis [beta blockers-antimalarial-lithium].
*the disease has a kobner phenomena [other diseases that have the same feature like lichen planus, vitiligo and wart.
Types of psoriasis....
1)classical type=psoriasis valguris
*involve extonsersurfac of elbow, knee joints,hands &
sacral areas
*there is no consistent laboratory finding but may be
raised uric acid level.
*treated with :-dithranol (anthrolin)
-topical steriod with or without tar and
salicylic acid.
-UV radiation
-PUVA,retinoids or cytotoxic drugs may
used in a serious psoriasis.
2)Guttate or rain drop psoriasis
*multiple small psoriatic lesions like drops mainly on the trunk proceeded by streptococcal throat infection.
*involve the abdomen and trunk.
*Can be miss diagnosed or mistaken with pityriasis roscea
*easly treated with UV radiation and mild tar based ontiment
3)scalp psoriasis
*it's difficult to diffrentiate between scalp psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis but psoriasis is generally thicker ,sever dandrof and temporary alopecia.
*treated with : tar shampoo- topical combination of tar and salicylic acid – topical steriods with or without salicylic acid.
4)nail psoriasis
*the finding are painful pitting & oncholysis[liftting of the nail plate or seperate of a part of nail bed.
*long standing psoriasis cause nail changes.
*treatment:nail changes not respod to topical treatment so systemic therapies may be helpful.
Other types:
5)psoriasis inversus 6)psoriatic arthropathy
7)palmoplantar psoriasis 8)napkin psoriasis
9)erythrodermic psoriasis
which type of psoriasis is dangerous?
Erythrodermic psoriasis is the dangerous type because it may cause electrolyte imbalance,heart failure,infection and hyponatremia.
What sites should be examined in a case of psoriasis?
Extonser surface of the knee and elbow,back, hands, sacral area, nail, scalp and feet.
Diffrential diagnosis of psoriasis....
1]discoid eczema 2]sebarrhoic eczema
3]pityriasis roscea 4]2ry syphilis
5]cutaneous T-cell lymphoma 6]tinea unguium
investigation...
1)biopsy[rarely needed] : will reveal pathological features
2)throat soap for streptococcal culture.
3)skin scraping to exclude tinea
4)rheumatoid factor to exclude psoriatic arthropathy
5)serological tests to exclude 2ry syphilis
treatment....
a-topical treatment:
1-emollients
2-tar:-it's a crude tar in a form of
an alcholic solution inhibits
DNA synthesis.
-side effects are:stain the cloths
smelly and can leads to folliculitis.
3-dithranol:-single most effective topical antipsoriatic treatment ,may cause staining and burning.
4-topical steriods
5-calcipotriol:(dovenex) not more than 100gm/week , act by inhibiting orthine decaeboxylase so decrease scale formation &erythema.
b- systemic treatment
1)PUVA[psoralen UVA]
*psoralen is taken 2-3 hrs before exposure to UVA
*psoralen is hepatotoxic so liver function test is lmportant
*long term exposure to radiation carry high risk of developing skin cancer.
*side effects of PUVA[erythema , itching and cataract].
2)retinoids
*it's a vitamin A derivatives
*may cause dry lips ,hair loss, teratogenic,hyperlipidemia ,liver impairment and renal impairment.
*liver function test,renal function test and lipid profile must be considered before beginning the treatment with retenoids.
3)cytotoxic drugs
liver function test and bone marrow function must be done before giving cytotoxic drugs.
4)cyclosporin
it's nephrotoxic and may cause high blood pressure.
5)systemic steroids.


No comments:
Post a Comment